YES! Fat plays an important role in our diet. The roles of fat include:
- Absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, such as Vitamin A, D, E, and K
- Keeps your hair, skin and nails healthy
- Provides calories that can be used for energy
- Stored to help insulate your body
- Brain development (in babies)
- Brain health (Omega-3 fats)
- Blood clotting
- Controls inflammation
However, there are different types of fat and it is sometimes difficult to know which fats are better to consume in moderation and which ones may cause future damage to the body if over-consumed. One of the worst kinds of fat for the body is trans fats, which should be avoided. Refer to the nutrition facts label and avoid trans fats and hydrogenated/partially-hydrogenated oils. The other types of fats are saturated and unsaturated. All fats contain both saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Fats are referred to as saturated or unsaturated depending on how much of the type of fatty acid they contain.1

Saturated Fat:

Avoid or limit foods high in saturated fats
- One of the worst kinds of fats for the body along with Trans fats
- According to the American Heart Association, “saturated fat can increase LDL, which is the bad cholesterol, decrease HDL, which is the good cholesterol, and increases the risk of heart disease and stroke”
- Sources: Animal products including butter, cheese, whole milk, ice cream, fatty/marbled cuts of meat skin of chicken/poultry and some vegetable oils, specifically coconut and palm oil and partially hydrogenated oils
- Tip: Fat is solid at room temperature
Unsaturated Fat:

Consume a variety and in moderation
- The healthier types of fats for the body
- Include polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats
- Help lower LDL, the bad cholesterol, raise your HDL, the good cholesterol, decrease the risk of heart attack and stroke, and provide the body with fats that it is unable to produce on its own.2
- Sources: plant based oils
- Monounsaturated fat: olive, canola, sunflower, peanut oil, nuts, and avocados
- Polyunsaturated fat: soybean, corn, safflower, walnuts, seeds, salmon, tuna, tofu
- Tip: Fat is liquid at room temperature
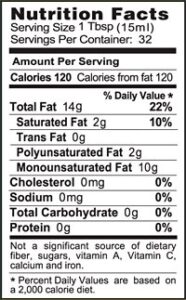
Selecting a Healthy Fat
When looking for a healthy fat it is best to look at the label to see which type of fats it contains in order to be sure that whatever is being consumed has a benefit to the body. The nutrition label can also be referred to for how many calories are in the oils, which may help with keeping a diet low in fat. On average, a teaspoon of oil contains 45 calories and a tablespoon of oil contains 150 calories. Overall, it is important to consume a variety of unsaturated fats and incorporate these healthy fats into your diet in moderation.
References
1. Dietary Fats Explained. MedlinePlus. Accessed April 24, 2018.
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000104.htm Accessed April 24, 2018
2. What are Oils? All about Oils. USDA ChooseMyplate
https://www.choosemyplate.gov/oils Accessed April 25, 2018
3. The American Heart Association Page. http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/HealthyLiving/HealthyEating/Nutrition/FATS-The-Good-the-Bad-and-the-Ugly-Infographic_UCM_468968_SubHomePage.jsp Updated 2014. Accessed April 24, 2018.
4. What Are Types of Fats?
https://www.move.va.gov/docs/NewHandouts/Nutrition/N09_WhatAreTheTypesOfFat.pdf Accessed April 25, 2018
Images:
http://chemicallabels-uk.com/chemical-hazard-symbols-labels/
https://pngtree.com/freepng/butter-butter_3292919.html
https://pngtree.com/freepng/olive-oil_1787340.html
Manage medical problems like high cholesterol, triglycerides or blood pressure, celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, diabetes, kidney disease, food allergies through medical nutrition therapy and teaching you:
- What to eat
- How much of your favorite foods you can eat
- Other lifestyle changes that will help you to manage your health problem
- What to eat
- When to eat
- How to hydrate for your event/sport

Our experienced Registered Dietitians provide needed services such as patient care, menu planning, standards evaluations, weight loss programs and wellness lectures to:
- Home Care agencies
- Drug and alcohol facilities
- Group Homes
- Wellness Programs within communities or businesses
- Community Programs
- Day care Centers
 Our weight loss program is not “a one size fits all” type of program. Each client is evaluated to determine their goals, there readiness to change, their confidence that they can change, what they know to change and what they need to learn to change. The program is structured according to what the client prefers or believes he/she will do the best with. Meal plans are provided as a guide when requested.
Our weight loss program is not “a one size fits all” type of program. Each client is evaluated to determine their goals, there readiness to change, their confidence that they can change, what they know to change and what they need to learn to change. The program is structured according to what the client prefers or believes he/she will do the best with. Meal plans are provided as a guide when requested.
Food diaries are strongly recommended, but not mandated, throughout the program.
 Individual Counseling:
Individual Counseling:
Many diseases we have inherited from our families can be prevented, delayed or reversed. For example if you have been told you have pre-diabetes, we can help you to make better food choices that will prevent you from having a diagnosis of diabetes.
Group Programs:
Our worksite programs which include: weight loss programs and various health and nutrition topics done as a interactive lectures or workshops. We work with your companies’ goals to prevent illness and lost productivity. Our family programs can take place in your home. We will help you to revise your meal choices and shopping to enhance your family’s health while taking your time limits and food preferences into consideration.
Cooking Classes:
Our “Cooking for One or Two” course was designed to help clients to eat healthy on a daily basis without a lot of time and work. The program meets twice a year in small groups of 5-7 clients. Clients can join for a one time session of 2 classes or twice a year for 4 classes.
 It surprises me that so many clients ask this question. Regardless of whether you have been diagnosed with diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or you are simply trying to lose weight, the food choices you make are fairly the same in order to eat and maintain a healthy diet. Below are some tips to help with making good choice when choosing when and how to eat.
It surprises me that so many clients ask this question. Regardless of whether you have been diagnosed with diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or you are simply trying to lose weight, the food choices you make are fairly the same in order to eat and maintain a healthy diet. Below are some tips to help with making good choice when choosing when and how to eat.
SCHEDULE EATING:
The most beneficial way to eat well is to have a regular eating schedule. This means eating within an hour of waking and every 3-5 hours after that. If it is convenient, eating 3 meals with a small snack in between can keep your energy up and help you avoid getting that starved feeling. If that is not realistic, at least plan to eat 3 meals and only have a snack when you are going longer than 4 hours between meals and know you will be hungry. For example, if your lunch is at noon and your dinner hour is 6 PM or later, 4 or 5 PM probably starve you. It is appropriate for you to have a snack to stave off hunger.
KEEP IT BALANCED:
A balanced meal has a source of protein, starchy vegetable or a grain (preferably a whole grain) and either a serving of a fruit or vegetable -or one of each. Fats and oils can be added in small amounts to enhance the meal. Balanced meals keep you full longer and help you feel more satisfied.
INCLUDE DAILY:
The following are the recommended amounts of each food group to include daily for adequate nutrition. Portions vary depending on ones age and sex. Amounts recommended daily are: fruits 1-2 cups, vegetables 1-3 cups a day, grains, 1 1/2 to 4 ounces, dairy 2 to 3 eight-ounce cups, protein (animal or vegetable) 2 oz. to 6 1/2 ounces, liquids oils 3 to 7 teaspoons. To learn what amount is appropriate for your age and sex, go to www.myplate.gov. If you have specific needs to manage diagnosis like diabetes, check with your registered dietitian to learn the best choices from these groups and the amounts appropriate for you.
SELECT HEALTHY SNACKS:
One should think of a snack as a “mini meal”. It should contain foods to hold you over to the next meal and also supply you with nutrients, not just “empty calories.”
The best foods for snacks are foods with fiber (fruits, vegetables, whole grains) and at times foods that have a small amount of protein to go along with it. A few examples are: a piece of fruit and 1 oz. cheese, whole grain crackers and 1 Tbsp peanut butter, or raw veggies and 1/4 cup humus.
Even with a diagnosed medical problem, snacks can be included. You would want to discuss snacks appropriate for your needs when you meet with your registered dietitian.
ENJOY TREATS ON OCCASION:
These are foods with little nutritional value, but ones you may enjoy occasionally. They would include cookies, chips, candy, and frozen desserts. The best way to include them in your diet is to have a serving at the end of a meal. If you are trying to lose weight, choose them less often and choose treats with fewer calories per serving. Most health problems requiring a special diet can include some type of treat food occasionally. If this is important to you, discuss it with your registered dietitian at your appointment.
 Each client’s program is unique to that client goals and what they are able to manage at that moment. With the client’s permission, we work closely with the other healthcare professionals providing care. This can include a physician, counselor, psychiatrist or others that the client would like us to interact with to help them to manage their disordered eating problem. When a meal plan is developed it is done in a gradual manner and and with client input.
Each client’s program is unique to that client goals and what they are able to manage at that moment. With the client’s permission, we work closely with the other healthcare professionals providing care. This can include a physician, counselor, psychiatrist or others that the client would like us to interact with to help them to manage their disordered eating problem. When a meal plan is developed it is done in a gradual manner and and with client input.

Manage medical problems
like high cholesterol, triglycerides or blood pressure, celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, diabetes, kidney disease, food allergies through medical nutrition therapy and teaching you:
- What to eat
- How much of your favorite foods you can eat
- Other lifestyle changes that will help you to manage your health problem
Lose weight
Whether a child or an adult, by providing direction to:
- Understand the issues that cause the extra weight
- Know what to eat to lose weight
- Know how much you need to eat to lose weight
- Understand how much physical activity can help you to lose and maintain the loss
Achieve your sports goals
with a nutrition plan that is specific for your chosen sport by providing guidelines on:
- What to eat
- When to eat
- How to hydrate for your event/sport
Recover from an eating disorder
by:
- Providing a meal plan specific for your nutritional and calorie needs
- Working with your team of doctor and counselor to help you become well and feel your best
What is Medical Nutrition Therapy?
Therapy prescribed for a medical diagnosis that is known to improve as the result of nutrition therapy. It includes
- A comprehensive nutrition assessment to determine the nutrition diagnosis
- Planning and implementing a nutrition intervention using evidence-based nutrition practice guidelines
- Monitoring and evaluating an individual’s progress over subsequent visits with the registered dietitian
Medical nutrition therapy is the essential therapy for:
- Type 1, Type 2 and Gestational diabetes
- Elevated cholesterol & triglycerides
- Food allergies and intolerances
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Celiac Disease
Medical nutrition therapy compliments:
- Psychotherapy for the treatment of eating disorders
- Pregnancy and nursing mothers
Medical Nutrition Therapy is covered by most Connecticut Insurances Companies






