YES! Fat plays an important role in our diet. The roles of fat include:
- Absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, such as Vitamin A, D, E, and K
- Keeps your hair, skin and nails healthy
- Provides calories that can be used for energy
- Stored to help insulate your body
- Brain development (in babies)
- Brain health (Omega-3 fats)
- Blood clotting
- Controls inflammation
However, there are different types of fat and it is sometimes difficult to know which fats are better to consume in moderation and which ones may cause future damage to the body if over-consumed. One of the worst kinds of fat for the body is trans fats, which should be avoided. Refer to the nutrition facts label and avoid trans fats and hydrogenated/partially-hydrogenated oils. The other types of fats are saturated and unsaturated. All fats contain both saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Fats are referred to as saturated or unsaturated depending on how much of the type of fatty acid they contain.1

Saturated Fat:

Avoid or limit foods high in saturated fats
- One of the worst kinds of fats for the body along with Trans fats
- According to the American Heart Association, “saturated fat can increase LDL, which is the bad cholesterol, decrease HDL, which is the good cholesterol, and increases the risk of heart disease and stroke”
- Sources: Animal products including butter, cheese, whole milk, ice cream, fatty/marbled cuts of meat skin of chicken/poultry and some vegetable oils, specifically coconut and palm oil and partially hydrogenated oils
- Tip: Fat is solid at room temperature
Unsaturated Fat:

Consume a variety and in moderation
- The healthier types of fats for the body
- Include polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats
- Help lower LDL, the bad cholesterol, raise your HDL, the good cholesterol, decrease the risk of heart attack and stroke, and provide the body with fats that it is unable to produce on its own.2
- Sources: plant based oils
- Monounsaturated fat: olive, canola, sunflower, peanut oil, nuts, and avocados
- Polyunsaturated fat: soybean, corn, safflower, walnuts, seeds, salmon, tuna, tofu
- Tip: Fat is liquid at room temperature
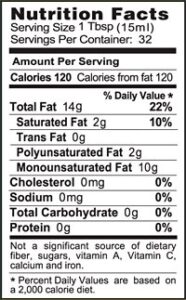
Selecting a Healthy Fat
When looking for a healthy fat it is best to look at the label to see which type of fats it contains in order to be sure that whatever is being consumed has a benefit to the body. The nutrition label can also be referred to for how many calories are in the oils, which may help with keeping a diet low in fat. On average, a teaspoon of oil contains 45 calories and a tablespoon of oil contains 150 calories. Overall, it is important to consume a variety of unsaturated fats and incorporate these healthy fats into your diet in moderation.
References
1. Dietary Fats Explained. MedlinePlus. Accessed April 24, 2018.
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000104.htm Accessed April 24, 2018
2. What are Oils? All about Oils. USDA ChooseMyplate
https://www.choosemyplate.gov/oils Accessed April 25, 2018
3. The American Heart Association Page. http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/HealthyLiving/HealthyEating/Nutrition/FATS-The-Good-the-Bad-and-the-Ugly-Infographic_UCM_468968_SubHomePage.jsp Updated 2014. Accessed April 24, 2018.
4. What Are Types of Fats?
https://www.move.va.gov/docs/NewHandouts/Nutrition/N09_WhatAreTheTypesOfFat.pdf Accessed April 25, 2018
Images:
http://chemicallabels-uk.com/chemical-hazard-symbols-labels/
https://pngtree.com/freepng/butter-butter_3292919.html
https://pngtree.com/freepng/olive-oil_1787340.html

